The cosine function is defined by the formula. The cosine function is a trigonometric function.

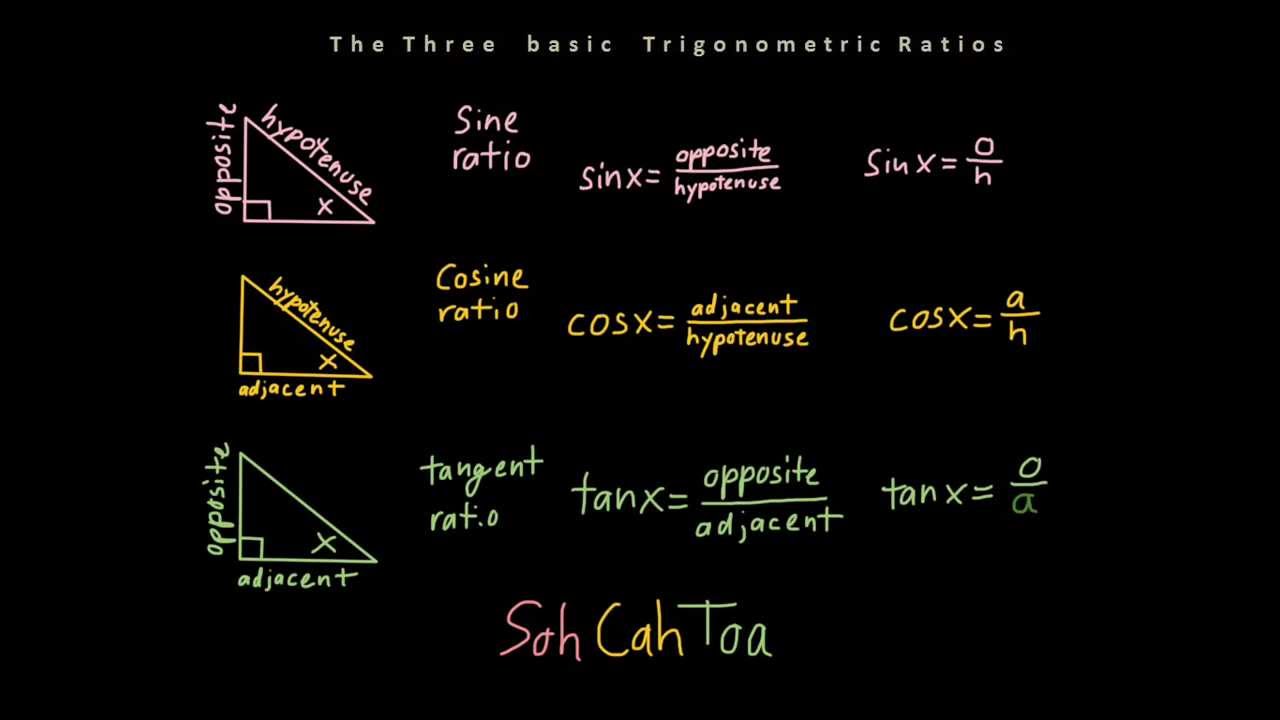
Soh Cah Toa Studying Math Math Methods Gcse Math
The Law of Cosines defines the relationship among angle measurements and lengths of sides in oblique triangles.

Cosine of right triangle. This tutorial shows you how to use the cosine ratio to find that missing measurement. In a right triangle how is the sine of one acute angle related to the cosine of the other acute angle. The Generalized Pythagorean Theorem is the Law of Cosines for two cases of oblique triangles.
Find the value of h. The cosine of a given angle in a right triangle is the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. In this section we will extend those definitions so that we can apply them to right triangles.
Then since the other angle is t. This function can be used to determine the length of a side of a triangle when given at least one side of the triangle. This definition however is incomplete and would not be found like this in Dutch school books for instance.
Let A and B be the two acute angles of a right triangle. The length of the adjacent side divided by the length of the hypotenuse. Cosine is usually shortened to cos but is pronounced cosine.
In finding the value of side b the two. Dropping an imaginary perpendicular splits the oblique triangle into two right triangles or forms one right triangle which allows sides to be related and measurements to be. When doing trigonometry in a classical way we consider a right angled triangle.
In a right triangle the side that is opposite of the 90 angle is the longest side of the triangle and is called the hypotenuse. The value of the sine or cosine function of t is its value at t radians. H sin64 18 h 18sin64 h 1618 Find the value of b.
What Is the Cosine Function. The Law of Cosines defines the relationship among angle measurements and lengths of sides in oblique triangles. Trigonometry is the study of the relationships within a triangle.
Simple turn the oblique triangle into a right triangle by drawing a line in the triangle. Trigonometry can also help find some missing triangular. In earlier sections we used a unit circle to define the trigonometric functions.
The Generalized Pythagorean Theorem is the Law of Cosines for two cases of oblique triangles. The Generalized Pythagorean Theorem is the Law of Cosines for two cases of oblique triangles. The cosine ratio is not only used to identify a ratio between two sides of a right triangle but it can also be used to find a missing side length.
The cosine is equal to the length of the side adjacent to the angle divided by the length of the hypotenuse. The cosine of an angle is found by relating the sides of a right triangle. In trigonometry the law of cosines is also known as the cosine formula or cosine rule relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles.
First we need to create our right triangle. Given ABC with A 47 B 68 and a 18. The Law of Cosines defines the relationship among angle measurements and lengths of sides in oblique triangles.
The cosine is also equal to the sine of the complementary angle. For right angled triangles the ratio between any two sides is always the same and are given as the trigonometry ratios cos sin and tan. Dropping an imaginary perpendicular splits the oblique triangle into two right triangles or forms one right triangle which allows sides to be related and measurements to be.
Figure PageIndex1 shows a point on a unit circle of. A right triangle is a type of triangle that has one angle that measures 90. The value of cos is commonly geven as the ratio adjacent side hypotenuse.
Dropping an imaginary perpendicular splits the oblique triangle into two right triangles or forms one right triangle which allows sides to be related and measurements to be. Cos adjacent hypotenuse. In a right angled triangle the cosine of an angle is.
Draw and label the triangle. The Cosine Function in Right Triangles Cosine is a trigonometric ratio comparing two sides of a right triangle. Using Right Triangles to Evaluate Trigonometric Functions.
Lets consider the following example. The abbreviation is cos. Right triangles and the relationships between their sides and angles are the basis of trigonometry.
8 7 b 8 8 b 7 2 The length of side b is 2212. They are always equal to each other.

Geometry Trigonometry Sine Cosine Tangent Task Cards Trigonometry Problem Based Learning Task Cards
Pin On Studypoint Sat Act Study Tips

Right Triangles And Trigonometry Graphic Organizer Reference Sheets Freebie Trigonometry Math Methods Gcse Math

Special Right Triangles Math Examples Trigonometry Worksheets Trigonometry

Right Triangle Trigonometry Worksheet Answers Trigonometry Worksheets Trigonometry Mathematics Education

Trig Special Right Triangles Special Right Triangle Right Triangle Triangle Math

Right Triangles Unit The Laws Of Cosines Sines Quiz Freebie Law Of Cosines Right Triangle Law Of Sines

Right Triangle Trig Trigonometry Right Triangle Love Math

Right Triangle Trigonometry Soh Cah Toa Doodle Graphic Organizer Packet Teaching Geometry Right Triangle Studying Math

Trig Ratio Handout Mathematics Worksheets Geometry Lessons Tangent

How To Use Sohcahtoa To Find The Trig Functions Of A Right Triangle Right Triangle Trigonometry Triangle Math

Right Triangle Trigonometry Soh Cah Toa Doodle Graphic Organizer Packet Trigonometry Math Notes Math Notebooks

Special Right Triangles Interactive Notebook Page Math Methods Teaching Geometry Teaching Math

A Quick Review Of Working With Sine Cosine Tangent A Plus Topper Tangent Triangle Abc Sines

A Right Triangle Def Is Shown To The Left Of The Text That Describes The Three Trigonometric Ratios The Sine Of Angle F Is Op Right Triangle Opposites Tangent

Trigonometry Non Right Angled Triangles Trigonometry Gcse Math Trigonometry Worksheets

Identify The Sides Of The Right Triangle Trigonometry Worksheets Mathematics Worksheets Trigonometry



